The Ultimate Guide to Ubuntu Commands for Beginners
Last Updated on August 24, 2022
What is Ubuntu?
Ubuntu is a free and open-source operating system. It is based on the Linux kernel and distributed with a GNU userland. Ubuntu has a wide range of support and can be installed on many different devices or used to power your own server. It is one of the best Linux distros used by developers. It has gained popularity because of how stable it is and how mature its package manager is.
Why Should You Learn These Commands?
Ubuntu commands are very important to learn because they can help you with almost anything you need to do on your computer.
They can help you fix any errors, install programs, and manage files. Learning these commands not only helps you navigate the command line interface but also helps you understand why some Linux commands are essential in operating a Linux operating system.
It shows how powerful a terminal can be since you can execute anything on the computer through the terminal. These tasks include changing file permissions, renaming files, check disk space just to name a few.
What are the Basic Ubuntu Commands?
Linux commands are a set of instructions that allow you to interact with the Linux operating system from the command line interface.
The Ubuntu commands helps you get around your system faster and more efficiently.
In this section, I am going to split the commands into their use cases.
Commands used for System Information
lsblk – List block devices on the system.
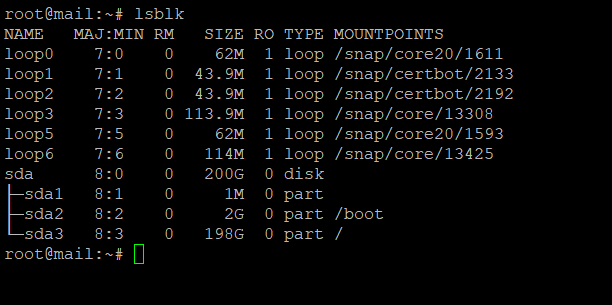
lspci – List all PCI devices in the system.
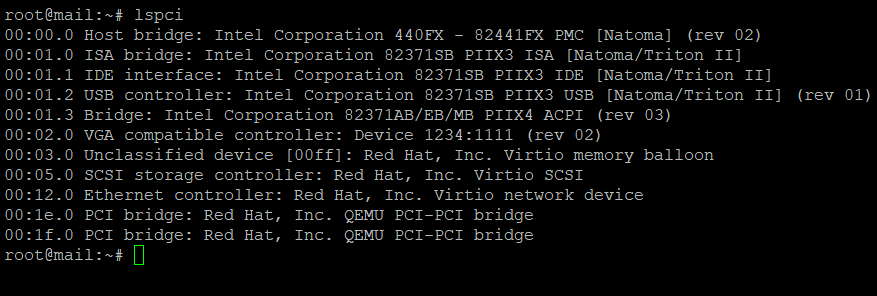
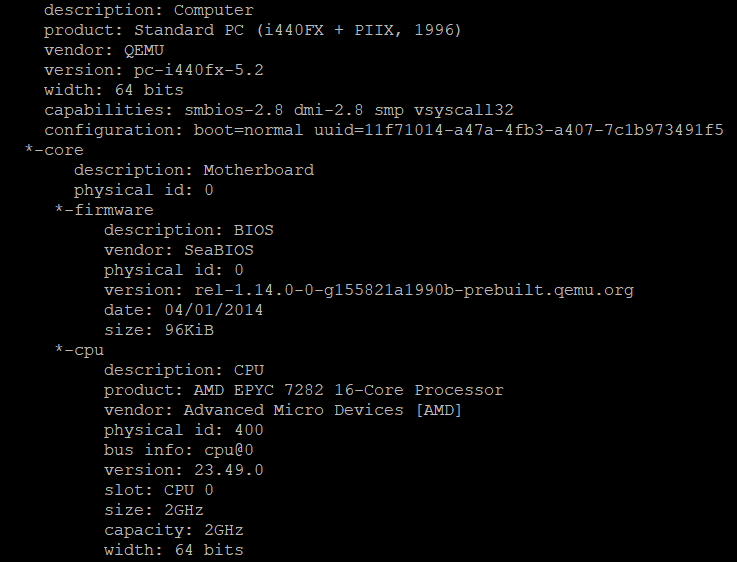
lshw – Show detailed hardware information about the machine.
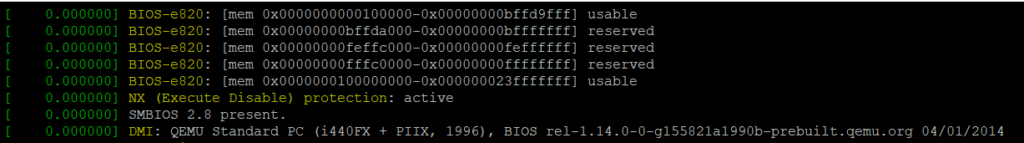
dmesg – Shows kernel messages since last boot.
uname – Displays the Linux kernel release and architecture.

Commands used for File Handling
The following commands are used for file handling.
ls: – Lists all the files and directories in the current directory.

touch: – Creates an empty file with a given name or alters a file’s timestamp to match that of a given date and time.
touch new.txtcp:- Copies a file from one place to another.
cp .env.example .env mv:- Moves and renames a file or directory.
mv directory/ /var/www/htmlrm:- Removes an existing file or directory.
rm new.txtfind:- Finds files in a directory and displays the names of those files.
find new.txtmkdir: – Creates a new directory
mkdir directoryrmdir: – Remove an empty directory.
rmdir directoryrd: – Removes a directory and all of its contents recursively.
rd directory/make:- Creates a new file in a specified location, which must exist and be empty.
make new.txtYou can read more on file permission commands here.
Ubuntu Commands For Package Installation
This is a list of commands which are the most useful for installing packages in Ubuntu. These commands will work in any Linux distribution, but the package names may be different.
apt-get install package name– Installs a package from the APT repository
apt-get update– Downloads the package lists from the repositories and “updates” them to get information on the newest versions of packages and their dependencies. Ideally, it updates the “links” of the packages from where the packages will be fetched when we perform an upgrade
apt-get upgrade – fetches new versions of packages existing on the operating system. This command now “upgrades” the packages by”following the links” that were updated using the apt-get update command
apt-get dist-upgrade – installs new packages or removes existing ones on its own during an upgrade
dpkg -i package-name– This command helps in installing Debian-based packages.
Download/Extract Files Via The Command Line On Ubuntu
wget
The wget command is an internet utility that can be used to download files from the web. It is a command line tool, which means it will only work in a terminal window. The wget command is very versatile and can be used to download files from different types of servers, as well as individual files from websites.
tar
The tar command is a computer program for packaging a set of files into a single file or multiple files. Tar can be used to create, extract, list and verify the contents of archives.
unzip
The unzip command is used to extract files from a ZIP archive. It can be used to extract the contents of an archive into the current directory, or into a new directory.
zip
Zip is a compression and archive format that was initially developed in the mid-1970s. It was created to replace the “archive” command which had been used on Unix systems.
The zip file format offers some advantages over tar and other formats: it can store many files, even if they are not part of a hierarchical directory tree, it provides better compression, especially for large files and it is supported on nearly all computing platforms.
Removing Packages/Uninstalling Software In Ubuntu
The following commands can be used to remove packages from your system:
apt-get remove package_name – removes installation files while keeping the configuration data for a package.
apt-get autoremove – removes packages that were automatically installed because some other package required them.
dpkg -P package_name – To uninstall a specific configuration file of a program
apt-get purge package_name – removes everything related to a package including the configuration files
apt-get autoclean – remove files that can no longer be downloaded and are deemed useless
Ubuntu/Linux Networking Commands
Below are some of the most common Linux networking commands you should know.
ifconfig– Configures interface information on a Linux system
ip addr show – Shows an IP address or a list of IP addresses associated with an interface
ifup – Configures network interfaces on a Linux system
Managing Processes, Closing Programs, And System Resources Commands
Managing processes, closing programs, and system resources are some of the basic tasks that Linux users need to perform on a regular basis. There are various commands that can be used to accomplish these tasks.
killall – kill all running process
pkill – kill process by name
ps – show the running processes
ps -ef – show all running processes and their command line arguments
kill – terminate the specified process ID (PID)
pgrep – find all instances of a particular process name, including those without a terminal or any open files. This is useful for finding runaway background processes
Ubuntu Authentication/User Account Commands
There are a few commands you can use to manage user accounts and authentication in Ubuntu.
passwd – you can use to change a user’s password
passwd usernameadduser – you can use to create a new user account
adduser usernamedeluser – you can use to delete an existing user account
deluser usernameFrequently Asked Questions
A working directory is a directory that contains the files that are currently in use by a process.
In Linux, it is the default location for storing temporary files and directories.
The working directory can be accessed using cd command or through the GUI of your Linux distribution.
To find out the filename in Linux, you can use the following command:
ls -l
There are many ways to search for a word within the Ubuntu terminal, but two of the most common are grep and locate.
Locate searches for files and directories in your computer’s file system, while grep searches for files in your computer’s data directory.
Ubuntu commands are case-sensitive. The command “ls” is different from the command “Ls” and the command “ls -l” is different from the command “Ls -l”.
In Closing
Ubuntu is one of the most popular Linux operating systems and is used by many hosting providers and companies in production. It is also used on desktops and as a result, understanding the basic commands can help you immensely.







